Optimize your food blog images for SEO and speed with our expert workflows. Learn ideal sizes, compression tools, and alt text tips to boost rankings.
Food blogging thrives on visuals. Mouthwatering images of sizzling dishes, vibrant ingredients, and beautifully plated meals draw readers in and keep them engaged. But stunning photos alone aren’t enough. Unoptimized images can slow your website, frustrate readers, and hurt your search engine rankings. Optimizing your food blog images is critical to balancing aesthetics with performance, ensuring your site loads quickly, ranks well on Google, and delights your audience. This comprehensive guide outlines the best workflows for optimizing food blog images, covering sizing, compression, file formats, SEO techniques, and tools to streamline the process.
Why Image Optimization Matters for Food Blogs
Food blogs are inherently visual. High-quality images showcase textures, colors, and the sensory experience of recipes, helping readers visualize the final dish. They also boost social media engagement, particularly on platforms like Pinterest and Instagram, driving traffic to your site. However, unoptimized images create significant challenges:
- Site Speed: Large image files increase page load times. Studies show 47% of users expect a page to load in 2 seconds or less, and 40% abandon sites that take longer than 3 seconds. Slow sites lose readers and rank lower on search engines.
- Server Resources: High-resolution images consume server storage and bandwidth, increasing hosting costs and potentially slowing down your entire site.
- SEO Impact: Search engines like Google prioritize fast-loading sites. Unoptimized images can negatively affect your rankings, while well-optimized images can improve visibility in Google Image Search.
- User Experience: Blurry or pixelated images (from being too small) or slow-loading images (from being too large) frustrate readers, especially on mobile devices or high-resolution screens like 4K or retina displays.
Optimizing images ensures they look crisp, load quickly, and enhance your site’s performance. This guide provides actionable workflows to achieve these goals, tailored specifically for food bloggers.
Step-by-Step Workflows for Image Optimization
1. Optimize Images Before Uploading
The first step in image optimization happens before your photos reach your website. Proper preparation ensures images are the right size, format, and quality, reducing the need for extensive post-upload processing.
Choose the Right File Format
Selecting the appropriate file format balances quality and file size. Here’s a breakdown of common formats for food blog images:
| Format | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| JPEG | Photographs, colorful food images | Smaller file size, good quality | Lossy compression can reduce quality if overdone |
| PNG | Logos, graphics, images with transparency | High resolution, sharp lines | Larger file sizes than JPEG |
| GIF | Simple animations, low-color images | Supports animations | Limited color range, larger file sizes |
For most food blog images, JPEG is the go-to format. It offers a good balance of quality and file size, making it ideal for vibrant food photos. Use PNG for graphics like logos or recipe cards with transparent backgrounds, but sparingly due to larger file sizes. Avoid GIF for food photos, as it’s better suited for animations.
Resize Images to Ideal Dimensions
Image dimensions (width and height in pixels) directly impact file size and display quality. For food blogs, the goal is to fill the content area of your blog posts without overloading the server.
- Recommended Width: 1200px is the gold standard for food blog images. This size accommodates most WordPress themes’ content areas (typically 600–800px wide) and looks crisp on high-resolution screens like retina displays.
- Height: Varies based on the image’s aspect ratio (e.g., 2:3, 16:9). Keep the aspect ratio locked during resizing to avoid distortion.
- Resolution: Set to 72 dpi for web images, as higher resolutions (e.g., 300 dpi) are unnecessary and increase file size.
| Image Type | Recommended Dimensions | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Blog Post | 1200px wide, height varies | Fits most content areas, scalable for responsive design |
| Featured Image | 1200 x 630px or 800 x 420px | Check theme documentation for exact sizes |
| Thumbnail | 400 x 400px | Used for previews, keeps file size small |
Use editing software like Adobe Photoshop, Lightroom, or free tools like GIMP or Canva to resize images. For example, if your original image is 3000 x 4500px, resizing to 1200px width will automatically adjust the height to 1800px for a 2:3 aspect ratio.
Adjust Export Quality
When exporting images, adjust the quality setting to reduce file size without compromising visual appeal. In Photoshop or Lightroom, quality settings range from 0% (lowest) to 100% (highest). A quality of 70–80% typically maintains clarity while significantly reducing file size. For example:
- A 1200 x 1800px JPEG exported at 100% quality might be 500KB.
- Reducing to 70% quality can bring it down to 200–250KB with minimal visible difference.
Experiment with quality settings to find the sweet spot for your photography style. Images with intricate details (e.g., a textured cake) may require higher quality to avoid blurriness.
Target File Size
Aim for a file size of 100–250KB per image. Files larger than 500KB slow down your site, while those under 100KB risk looking pixelated on high-resolution screens. After exporting, check the file size in your file explorer or editing software. If it’s too large, reduce the quality setting or further compress the image.
Name Images Descriptively
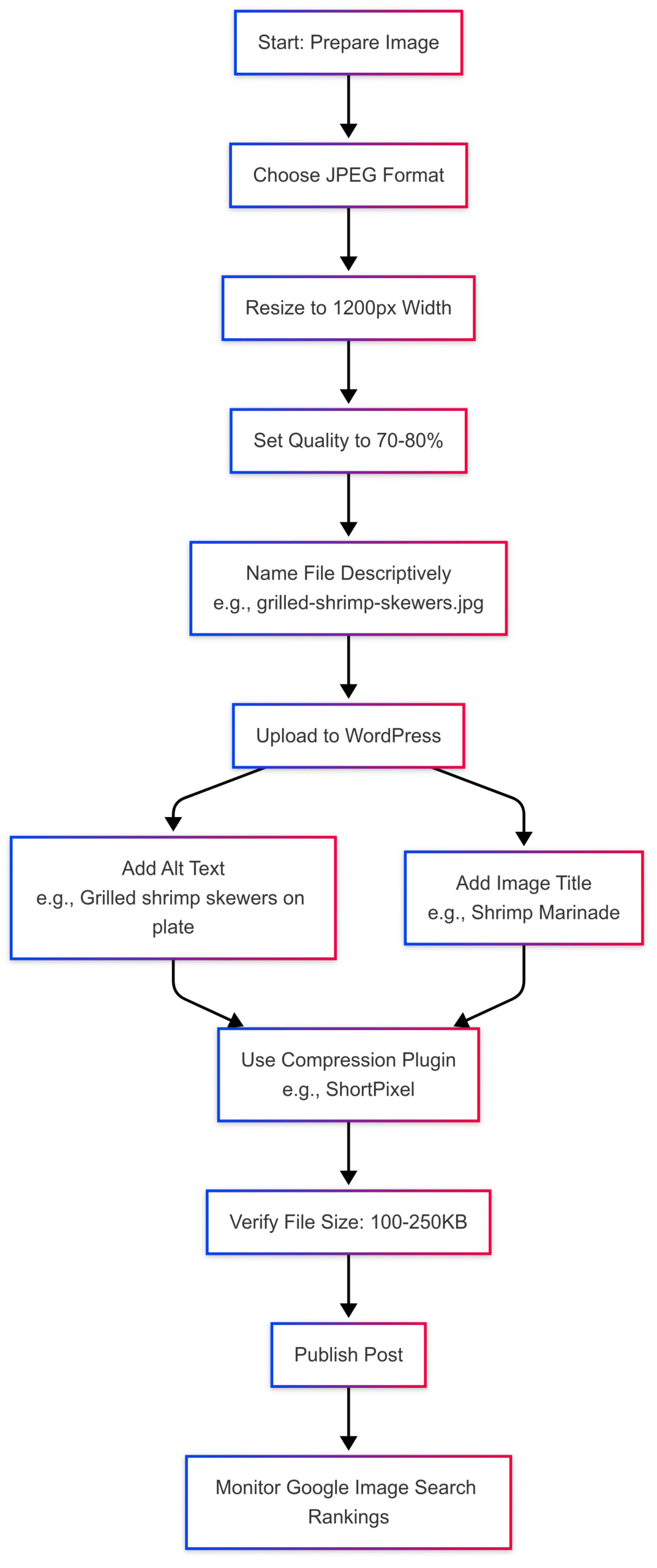
File Naming impacts SEO and organization. Instead of generic names like IMG_1234.jpg, use descriptive, keyword-rich names with hyphens, such as grilled-shrimp-skewers.jpg. This helps Google understand the image content and improves discoverability in image search results.
Example Workflow in Photoshop:
- Open your image in Photoshop.
- Go to
File > Export > Save for Web (Legacy). - Set the format to JPEG.
- Adjust the width to 1200px, keeping the aspect ratio locked.
- Set quality to 70–80%.
- Save as
recipe-name.jpg(e.g.,chocolate-cake-recipe.jpg). - Verify the file size is 100–250KB.
2. Optimize Images in WordPress
Once images are uploaded to WordPress, additional optimization ensures they perform efficiently across devices.
Use a Compression Plugin
Compression plugins reduce file sizes further and optimize WordPress-generated thumbnails (e.g., 150px, 600px, 1024px versions created via the srcset attribute). Popular plugins include:
| Tool | Type | Best For | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| ShortPixel | WordPress Plugin | Automatic compression, bulk optimization | Free (100 images/month), Paid ($4.99/month for 7,000 images) |
| Imagify | WordPress Plugin | High-quality compression, WebP support | Free (20MB/month), Paid ($4.99/month for 500MB) |
| Smush | WordPress Plugin | Automatic resizing and compression | Free, Pro ($7.50/month) |
| Cloudflare Enterprise | Hosting Add-on | Advanced optimization, CDN delivery | Varies by hosting provider (e.g., Bigscoots) |
For food bloggers, ShortPixel and Imagify are excellent choices for their robust compression algorithms and support for modern formats like WebP. If you use a hosting provider like Bigscoots with Cloudflare Enterprise, its built-in image optimization may eliminate the need for a separate plugin.
How Compression Plugins Work
- Automatic Compression: Plugins like Smush compress images upon upload, reducing file size without manual intervention.
- Bulk Optimization: Optimize existing images in your media library.
- Thumbnail Optimization: Compress WordPress-generated thumbnails for faster loading across devices.
- Lossy vs. Lossless: Lossy compression (e.g., ShortPixel’s “Glossy” mode) reduces file size more but may slightly affect quality. Lossless compression preserves quality but results in larger files.
Example Workflow with ShortPixel:
- Install and activate ShortPixel.
- Go to
Settings > ShortPixeland configure compression settings (e.g., Glossy for food photos). - Upload images to WordPress.
- Run bulk optimization to compress existing images.
- Verify file sizes in the media library (aim for 100–250KB).
Leverage WordPress srcset
WordPress’s srcset attribute automatically serves different image sizes based on the user’s device. For example, a 1200px-wide image might be served at 600px for a smartphone. Ensure your theme supports srcset (most modern themes do) to optimize for responsive design.
3. Optimize Images for SEO
Image optimization isn’t just about speed—it’s also about improving your blog’s visibility on search engines.
Add Descriptive Alt Text
Alt text (alternative text) describes the image for screen readers and search engines. It’s essential for accessibility and SEO. Write concise, descriptive alt text that captures the image’s content without stuffing keywords.
- Good Example:
Grilled shrimp skewers on a white plate with lemon wedges - Bad Example:
Shrimp recipe for summer BBQ with delicious marinade
Insert alt text in WordPress:
- Upload the image to your post.
- Click the image in the media library or block editor.
- Add alt text in the “Alt Text” field (e.g.,
Chocolate chip cookies on a cooling rack).
Use Meaningful Image Titles
Image titles in WordPress (distinct from file names) provide additional context for search engines. Keep them general but descriptive, like Shrimp Marinade or Homemade Pizza. Add titles in the WordPress media library when uploading.
Optimize for Google Image Search
Keyword-rich file names, alt text, and titles help images rank in Google Image Search, driving traffic to your blog. For example, an image named vegan-chocolate-cake.jpg with alt text Slice of vegan chocolate cake with raspberries is more likely to appear in relevant searches.
Chart: Image SEO Workflow
4. Optimize Images for Pinterest
Pinterest is a visual platform where food bloggers can drive significant traffic. Optimizing images for Pinterest requires specific dimensions and tools.
Ideal Pinterest Image Sizes
- Standard Pins: 1000 x 1500px (2:3 aspect ratio)
- Square Pins: 1000 x 1000px
- Infographic Pins: 1000 x 2000px or taller
Use Tasty Pins ($49/year, 14-day money-back guarantee), a WordPress plugin designed for Pinterest optimization. It allows you to:
- Set Pinterest-specific alt text and descriptions.
- Disable pinning for non-relevant images.
- Add hidden Pinterest images to posts.
Example Workflow with Tasty Pins:
- Install Tasty Pins in WordPress.
- Upload a 1000 x 1500px image (e.g.,
vegan-pasta-recipe-pin.jpg). - Add Pinterest-specific alt text (e.g.,
Vegan pasta with tomato sauce in a bowl). - Set a Pinterest description (e.g., “Try this easy vegan pasta recipe!”).
- Publish and share the pin on Pinterest.
5. Tools for Streamlined Optimization
The right tools make image optimization efficient and hassle-free. Here’s a comparison of top tools:
| Tool | Type | Best For | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photoshop | Desktop Software | Professional editing, resizing | $22.99/month (Adobe Creative Cloud) |
| Canva | Online Design Tool | Creating and resizing images | Free, Pro ($14.99/month) |
| ILoveIMG | Online Tool | Bulk compression, resizing | Free, Premium ($4/month) |
| TinyPNG | Online Tool | Compressing individual images | Free (20 images/month), Paid ($39/year) |
| Tasty Pins | WordPress Plugin | Pinterest optimization | $49/year |
Recommended Workflow:
- Edit and resize images in Canva or Photoshop (1200px width, 70–80% quality).
- Compress images with ILoveIMG or TinyPNG to 100–250KB.
- Upload to WordPress and optimize with ShortPixel or Imagify.
- Add SEO-friendly alt text and titles.
- Use Tasty Pins for Pinterest optimization.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Over-Compression: Compressing images too much can lead to blurriness. Test quality settings to maintain clarity.
- Small Dimensions: Images under 600px wide appear pixelated on retina screens. Stick to 1200px width.
- Generic File Names: Avoid names like
IMG_1234.jpg. Use descriptive names for SEO. - Ignoring Theme Settings: Check your WordPress theme’s recommended image sizes to avoid distortion.
- Skipping Alt Text: Always add alt text for accessibility and SEO.
Measuring Success
After optimizing images, monitor your site’s performance:
- Site Speed: Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights or GTmetrix to check load times.
- SEO Rankings: Track image rankings in Google Image Search using Google Search Console.
- Traffic: Analyze Pinterest and image search traffic in Google Analytics.
Conclusion
Optimizing food blog images is a critical workflow that enhances site speed, improves SEO, and elevates user experience. By resizing images to 1200px width, using JPEG format, compressing to 100–250KB, adding descriptive alt text and titles, and leveraging tools like ShortPixel and Tasty Pins, you can ensure your images are both beautiful and efficient. Implement these strategies to make your food blog faster, more discoverable, and more engaging for your readers.
Please share these Best Workflows for Optimizing Your Food Blog Images with your friends and do a comment below about your feedback.
We will meet you on next article.
Until you can read, Best Artificial Lights for Food Photography
