Master Google AdSense for your food blog! Learn setup, ad management, and monetization tips to boost revenue with our comprehensive guide.
For food bloggers, creating mouthwatering recipes and stunning food photography is only part of the journey. Turning your passion into a sustainable income stream is the next step, and Google AdSense offers a powerful way to achieve that. This comprehensive guide dives deep into how food bloggers can leverage Google AdSense to monetize their blogs effectively. From setting up an account to optimizing ad placements and navigating approval challenges, we’ll cover everything you need to know to succeed—while avoiding pitfalls like irrelevant ads (think earwax removal on a vegan recipe blog). Let’s explore how to make Google AdSense work for your food blog.
What is Google AdSense?
Google AdSense is an advertising program that allows bloggers and website owners to earn revenue by displaying targeted ads on their sites. Advertisers bid through Google’s ad auction to place their ads, which are then matched to your blog’s content using keyword analysis and user behavior data. When visitors click on these ads or, in some cases, view them, you earn a portion of the revenue. For food bloggers, AdSense is appealing because it’s free, relatively easy to set up, and integrates seamlessly with platforms like WordPress, YouTube, and other content management systems.
The program’s strength lies in its ability to serve contextually relevant ads. For example, a recipe for vegan ramen might display ads for plant-based ingredients or kitchen tools. However, as we’ll discuss, this system isn’t foolproof, and food bloggers must actively manage ad content to ensure relevance and maintain a positive user experience.
Why Food Bloggers Should Consider Google AdSense
AdSense is a popular choice for food bloggers because it offers passive income potential with minimal upfront costs. Unlike affiliate marketing or sponsored posts, which require ongoing negotiations, AdSense automates ad delivery, allowing you to focus on creating recipes and engaging content. However, food blogs face unique challenges, such as high competition and strict approval criteria, which we’ll address throughout this guide.
Here’s a quick breakdown of why AdSense is worth considering:
- Ease of Use: Simple setup process with Google’s step-by-step guidance.
- Passive Income: Earn money without actively managing ad campaigns.
- Scalability: As your traffic grows, so does your revenue potential.
- Integration: Works seamlessly with popular platforms like WordPress.
However, food blogs, particularly recipe-focused ones, often struggle with AdSense approval due to market saturation. Later, we’ll explore strategies to overcome this and alternative monetization options.
Setting Up Your Google AdSense Account
Step 1: Create a Google Account
To use AdSense, you need a Google account. If you don’t have one, sign up at accounts.google.com. This account will be your gateway to AdSense and other Google tools.
Step 2: Apply for AdSense
Visit the Google AdSense Get Started page and click the “Get Started” button. You’ll need to provide:
- Your website URL.
- Basic personal and payment information.
- Agreement to AdSense’s terms and conditions.
After submitting your application, Google reviews your site to ensure it meets their policies. This process can take a few days to a few weeks, so patience is key.
Step 3: Install AdSense Code
Once approved, you’ll receive instructions to add AdSense code to your blog. The process varies by platform:
- WordPress: Use a plugin like Site Kit by Google or manually insert the code via a Custom HTML widget.
- YouTube: Link your channel to AdSense through YouTube Studio.
- Other Platforms: Follow platform-specific guides available on Google’s support pages.
Approval Challenges for Food Blogs
Google AdSense has strict criteria, and food blogs often face rejections due to:
- Lack of Original Content: Generic recipes or “scraped” content (reposted or slightly rewritten from other sources) are red flags.
- Insufficient Content: New blogs with few posts (e.g., fewer than 20–50 high-quality articles) are often rejected.
- Low Traffic: Sites with minimal organic search traffic struggle to gain approval.
- Niche Saturation: The recipe niche is highly competitive, making it harder to stand out.
To improve your chances, aim for 50+ original posts of 800+ words each, published consistently over 3–6 months. Ensure your content is unique, engaging, and adds value—think detailed guides, personal stories, or niche recipes (e.g., gluten-free vegan desserts).
Manual vs. Auto Ads: Which Should You Choose?
AdSense offers two ways to display ads: Manual and Auto Ads. Each has pros and cons, especially for food bloggers who prioritize aesthetics and user experience.
Manual Ads
With Manual Ads, you create specific ad blocks on your blog using a Custom HTML widget (on WordPress) or similar tools on other platforms. You control:
- Ad Type: Choose between display ads (banners), in-feed ads (blending with content), or in-article ads (within posts).
- Ad Size: Select sizes like 300×250 (rectangle) or 728×90 (leaderboard).
- Ad Placement: Decide where ads appear, such as sidebars, headers, or between paragraphs.
Pros:
- Greater control over ad aesthetics and placement.
- Avoids cluttering your blog with excessive ads.
- Maintains a professional look aligned with your brand.
Cons:
- Time-consuming to set up and optimize.
- May not fully leverage Google’s ad optimization algorithms.
Auto Ads
Auto Ads let Google’s algorithms decide ad type, size, and placement based on your site’s layout and traffic patterns. You add a single code snippet to your site, and Google handles the rest.
Pros:
- Quick and easy setup.
- Optimizes ad performance automatically.
- Adapts to changes in traffic and content.
Cons:
- Less control over ad placement and aesthetics.
- Risk of irrelevant or intrusive ads (e.g., the infamous earwax ad).
Recommendation for Food Bloggers
For beginners or those with limited coding skills, Auto Ads are a good starting point due to their simplicity. However, experienced bloggers may prefer Manual Ads to maintain a polished look, especially since food blogs rely heavily on visuals. A hybrid approach—starting with Auto Ads and gradually transitioning to Manual Ads as you learn—can balance ease and control.
Here’s a comparison table:
| Feature | Manual Ads | Auto Ads |
|---|---|---|
| Setup Time | High (requires manual coding) | Low (single code snippet) |
| Control | Full control over type/placement | Limited control |
| Optimization | User-driven | Algorithm-driven |
| Best For | Experienced bloggers | Beginners or time-constrained users |
Managing Ad Content: Avoiding the Earwax Ad Fiasco
One of the biggest challenges food bloggers face with AdSense is irrelevant ads. Imagine a vegan recipe blog displaying ads for earwax removal or pest control—hardly appetizing! Fortunately, AdSense provides tools to manage ad content.
Using the Ad Review Center
The Ad Review Center, accessible via the “Blocking Controls” menu in your AdSense dashboard, lets you:
- View ads currently displayed on your site.
- Block specific ads by clicking the “block” symbol.
- Review similar ads and block them preemptively.
For example, you can block ads for medical procedures or unrelated products to keep your blog on-brand. Regularly check the Ad Review Center to ensure ads align with your food-focused content.
Blocking Advertiser URLs
Blocking individual ads is effective but temporary, as advertisers often create new variations. A more robust solution is blocking entire advertiser URLs:
- Go to “Blocking Controls” > “All Sites” in your AdSense dashboard.
- Select “Manage Advertiser URLs.”
- Add the root URL of the advertiser (e.g.,
earwaxremoval.com).
This prevents all ads from that advertiser, ensuring your blog remains free of irrelevant promotions.
Tips for Content Control
- Keyword Optimization: Use specific, food-related keywords in your content to attract relevant ads (e.g., “vegan baking” or “gluten-free recipes”).
- Category Blocking: Block ad categories like health or home improvement that don’t suit a food blog.
- Monitor Regularly: Check your site weekly for new ad content, especially after adding new posts.
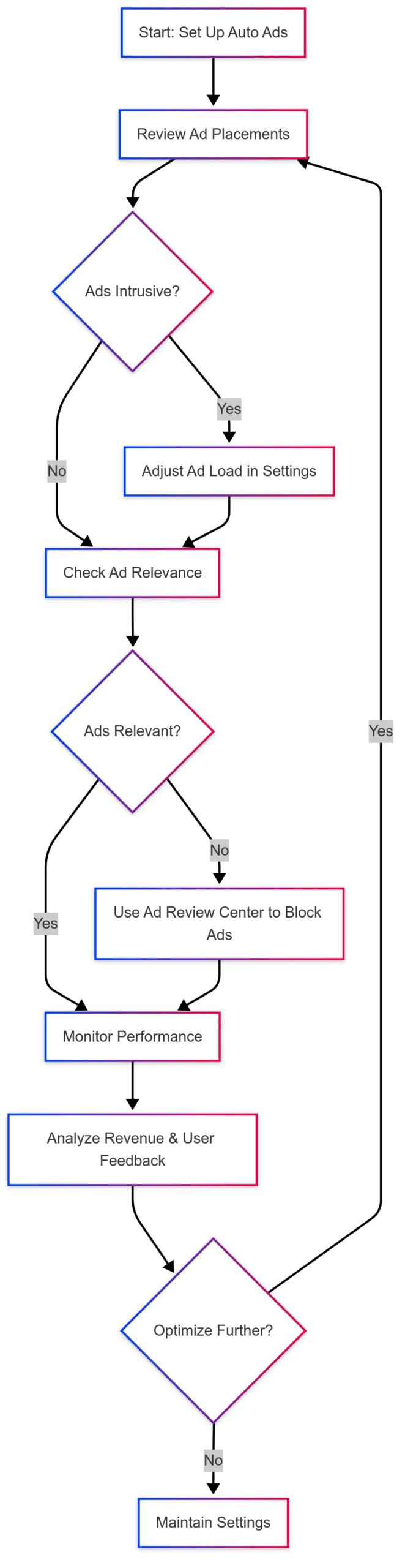
Optimizing Ad Placement for User Experience
Ad placement is critical for balancing revenue and user experience. Too many ads can frustrate visitors, causing them to leave before finding your recipes. Here’s how to optimize placement, especially with Auto Ads:
- Access Ad Settings: Go to the “Ads Overview” tab in your AdSense dashboard, select your site, and click the pencil icon to edit settings.
- Adjust Ad Load: Control the number of ads displayed per page. For food blogs, aim for 2–4 ads to avoid overwhelming users.
- Choose Ad Formats: Enable formats like in-article or in-feed ads, which blend better with recipe content than large banners.
- Exclude Pages: Prevent ads on non-monetizable pages like “About” or “Contact” to comply with AdSense policies.
Here’s a Mermaid chart illustrating the ad optimization process:
Overcoming AdSense Approval Challenges for Food Blogs
Food blogs, especially recipe sites, face high rejection rates from AdSense due to niche saturation. Google prioritizes sites with:
- Unique Content: Avoid generic recipes. Add personal stories, unique techniques, or niche focuses (e.g., vegan keto).
- Sufficient Content: Aim for 50+ posts of 800+ words, published weekly for 3–6 months.
- Organic Traffic: Use SEO tools to drive traffic through search engines.
- Technical Compliance: Ensure your site is crawlable (e.g., no restrictive robots.txt) and has a sitemap.
Case Study: Herbivore’s Kitchen
Kate Friedman, creator of Herbivore’s Kitchen, a vegan food blog, faced an AdSense mishap when an earwax removal ad appeared in her site’s header. Her mistake? Rushing into Auto Ads without understanding content controls. After blocking irrelevant ads and URLs, she optimized her ad settings to align with her vegan audience, boosting both revenue and user satisfaction.
Alternatives to Google AdSense
Given AdSense’s strict approval process, food bloggers may explore alternatives like Mediavine or AdThrive. These networks often have higher payout rates but also require AdSense approval as a prerequisite.
Mediavine vs. AdSense
Mediavine is a popular choice for food bloggers, offering:
- Higher Revenue: Better CPM rates than AdSense.
- Food Blog Focus: Tailored for recipe sites with strong traffic (50,000+ monthly sessions).
- AdSense Requirement: You must be an AdSense-approved publisher in good standing.
Interestingly, some Mediavine-approved sites have basic content, suggesting that consistent posting and traffic matter more than groundbreaking originality. To apply for Mediavine, ensure your site meets their traffic threshold and has a clean AdSense history.
Other Monetization Strategies
- Affiliate Marketing: Promote food-related products (e.g., kitchen gadgets) through Amazon Associates or other programs.
- Direct Ad Placements: Partner with food brands for custom ads.
- Digital Products: Sell cookbooks, meal plans, or online courses.
- Sponsored Posts: Collaborate with brands for paid content.
Here’s a comparison of monetization options:
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Google AdSense | Easy setup, passive income | Strict approval, lower payouts |
| Mediavine | Higher payouts, food blog-friendly | High traffic requirement |
| Affiliate Marketing | Flexible, high potential earnings | Requires active promotion |
| Direct Ads | High control, brand alignment | Time-intensive negotiations |
Maximizing Revenue with Google AdSense
To boost your AdSense earnings:
- Focus on SEO: Optimize posts for high-traffic keywords like “easy vegan recipes” or “gluten-free desserts.”
- Increase Traffic: Share content on social media and Pinterest to drive clicks.
- Test Ad Formats: Experiment with in-article vs. in-feed ads to find what works best.
- Monitor Analytics: Use AdSense reports to track performance and adjust strategies.
For example, a food blog with 10,000 monthly page views earning a $5 CPM (cost per thousand impressions) could generate $50/month. Scaling to 50,000 page views could yield $250/month, highlighting the importance of traffic growth.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Irrelevant Ads: Regularly use the Ad Review Center and block URLs to maintain relevance.
- Overloading Ads: Limit ad load to preserve user experience.
- Policy Violations: Avoid prohibited content (e.g., copyrighted recipes) to prevent account bans.
- Rushing the Process: Build a robust site with 50+ posts before applying.
Final Thoughts: Building a Monetized Food Blog
Google AdSense is a powerful tool for food bloggers seeking passive income, but it requires strategic setup and ongoing management. By creating high-quality, original content, optimizing ad placements, and exploring alternatives like Mediavine, you can turn your food blog into a revenue-generating machine. Start by building a strong content foundation, apply for AdSense with confidence, and use the tools provided to ensure ads enhance—rather than detract from—your readers’ experience.
For more tips on food blogging, explore topics like recipe development, food photography, and alternative monetization strategies. Have questions or a success story to share? Drop them in the comments below!
Please share these A Food Blogger’s Guide to Google AdSense with your friends and do a comment below about your feedback.
We will meet you on next article.
Until you can read, Journey by Mediavine for Food Bloggers
