5 Proven Ways to Make Money with Food
Discover 5 proven ways to make money with food, from food blogging to catering, with practical steps to turn your culinary passion into profit.
The culinary world offers endless opportunities for those who love food to transform their passion into a profitable venture. Whether you’re a home cook, a professional chef, or an aspiring entrepreneur, the food industry provides diverse avenues to generate income.
This comprehensive guide explores five proven strategies to make money with food, offering practical steps, expert insights, and actionable tips to help you succeed. From launching a food blog to starting a catering business, these methods cater to various skill levels, budgets, and time commitments. Let’s dive into how you can turn your culinary skills into a thriving business.
1. Choose a Profitable Food Business Model
Selecting the right business model is the foundation of a successful food venture. The profitability of food businesses often depends on the type of products or services offered, the target market, and the operational scale. Below, we explore high-margin food items, various business models, and the regulatory considerations to ensure compliance and success.
High-Margin Food Products
Certain food items stand out for their profitability due to low production costs, high demand, and scalability. Here are some of the most lucrative options:
- Specialty Baked Goods: Custom celebration cakes (e.g., wedding or birthday cakes) can yield 50-60% profit margins due to their premium pricing and relatively low ingredient costs. Artisanal breads and dietary-specific desserts (gluten-free, vegan, or keto) offer 10-15% margins, appealing to niche markets with health-conscious consumers.
- Gourmet Sauces and Preserves: Small-batch hot sauces, unique jams, and specialty condiments like infused oils can achieve up to 60% margins. These products require minimal equipment and can be produced in small quantities, making them ideal for home-based businesses.
- Custom Meal Prep Services: Ready-to-eat meals tailored to specific diets (keto, vegan, high-protein) have 20-25% margins. These services cater to busy professionals and fitness enthusiasts who value convenience and nutrition.
- Specialty Snacks and Beverages: Artisanal popcorn, flavored nuts, kombucha, and fresh-pressed juices offer 20-25% margins. These products are popular at farmers’ markets and online platforms due to their portability and appeal.
Table 1: Profit Margins of Popular Food Products
| Product Type | Profit Margin | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Custom Celebration Cakes | 50-60% | High labor, premium pricing |
| Artisanal Breads/Desserts | 10-15% | Niche markets, dietary-specific demand |
| Gourmet Sauces/Preserves | Up to 60% | Low equipment costs, scalable production |
| Custom Meal Prep Services | 20-25% | High demand, subscription potential |
| Specialty Snacks/Beverages | 20-25% | Portable, popular at markets and online |
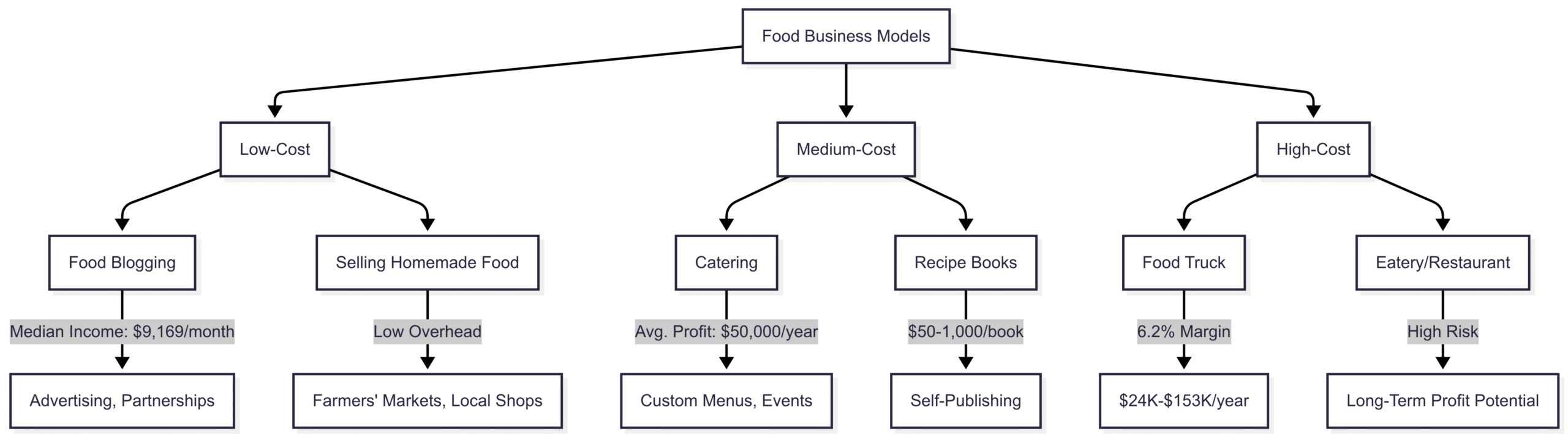
Business Models for Different Budgets
Food businesses vary in startup costs and scalability. Here are low, medium, and high-cost models to consider:
Low-Cost Business Ideas
- Food Blogging: Starting a food blog is a low-cost entry point with significant earning potential. Successful food bloggers earn a median monthly income of $9,169 through advertising (42-44% of revenue), online courses, brand partnerships, and affiliate marketing. Initial earnings of $100-300 typically begin after 6-12 months, with $1,000-3,000 monthly after 1-2 years. Brett Lindenberg, founder of Food Truck Empire, notes that many bloggers invest three years before earning $20,000-$40,000 annually.
- Selling Homemade Food: Begin by selling to friends, family, or local communities, then scale to farmers’ markets or local shops. Products like baked goods, jams, or snacks are ideal for home kitchens, requiring minimal equipment and offering flexible schedules.
Medium-Cost Business Ideas
- Catering: Catering can generate significant profits, with professionals like Aaliyah Patel reporting average annual profits of $50,000. A unique menu with signature dishes can attract repeat clients for events like weddings or corporate gatherings. Startup costs include equipment and marketing, but the flexibility to choose event sizes makes it manageable.
- Recipe Books: Self-publishing a cookbook, either digital or print, can yield $50-1,000 monthly per book. Jason Logsdon of Amazing Food Made Easy earned $700 from e-book sales and $2,250 from print sales for a book published years earlier. This model suits creative cooks with strong writing skills.
High-Cost Business Ideas
- Food Truck: A food truck offers mobility and flexibility, with profit margins around 6.2% and annual incomes ranging from $24,000 to $153,000. Costs include purchasing or remodeling a vehicle and equipping a mobile kitchen, but the ability to move to high-traffic locations boosts revenue potential.
- Eatery/Restaurant: Opening a restaurant is capital-intensive and challenging, with high failure rates (as seen in Kitchen Nightmares). However, with experience, a unique concept, and effective management, it can become profitable long-term.
Chart: Food Business Model Comparison
Regulatory Considerations
Compliance with food safety regulations is critical for businesses selling food directly to consumers. Requirements vary by region:
- United States: Cottage food laws allow home-based production of shelf-stable items like baked goods and jams, but regulations differ by state. Check with your local health department for permits and restrictions.
- United Kingdom: Register with the Food Standards Agency 28 days before starting operations. Home kitchens must meet hygiene standards and pass inspections.
- European Union: Register with local health authorities and comply with EU food safety regulations, including labeling and allergen information.
Food bloggers and cookbook authors typically don’t need permits unless selling physical products. Always consult local authorities to ensure compliance.
Market Research for Success
Before launching, conduct thorough market research to validate your idea:
- Identify Your Target Audience: Analyze demographic data (age, income, dietary preferences) to tailor your offerings. For example, keto meal prep services appeal to fitness enthusiasts, while vegan desserts attract health-conscious consumers.
- Analyze Competitors: Study successful businesses to identify gaps in the market. What unique value can you offer? For instance, a local bakery might lack gluten-free options, creating an opportunity.
- Assess Demand: Use surveys, social media polls, or focus groups to gauge interest in your products. Test small batches at local markets to collect feedback.
2. Build a Strong Online Presence
In today’s digital age, an online presence is essential for reaching customers and building a brand. A well-crafted online strategy can transform a small food business into a profitable enterprise.
Develop a Compelling Brand
Your brand is more than a logo—it’s the story of your food. What makes your recipes or products unique? Are you focused on sustainability, local ingredients, or innovative flavors? Create a consistent brand voice and visual identity across all platforms. For example, a vegan bakery might emphasize eco-friendly packaging and plant-based ingredients to attract environmentally conscious customers.
Create a Professional Website
A user-friendly website is the cornerstone of your online presence. Platforms like WordPress offer customizable themes tailored for food businesses. Key features to include:
- Food Safety Information: Display allergen lists and handling procedures to build trust.
- Delivery Parameters: Clearly state delivery zones and shipping limitations.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: Over 70% of food orders come through mobile devices, so ensure your site is responsive.
- Ordering System: Use plugins like WooCommerce for seamless e-commerce integration, as seen on The Minimalist Baker.
Professional food photography is critical. Use a smartphone with natural daylight, white plates, and simple backgrounds to create appetizing images. WP Recipe Maker enhances recipe blogs with features like adjustable servings, affiliate links, and SEO-optimized metadata.
Table 2: Essential Website Features for Food Businesses
| Feature | Purpose | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Food Safety Info | Builds customer trust | Allergen lists, certifications |
| Delivery Parameters | Clarifies service scope | Shipping maps, radius info |
| Mobile-Friendly Design | Enhances user experience | WordPress responsive themes |
| Ordering System | Streamlines sales | WooCommerce, Shopify |
| Recipe Cards | Improves engagement, SEO | WP Recipe Maker |
Implement SEO Best Practices
Search engine optimization (SEO) drives organic traffic to your website. Food-specific SEO strategies include:
- Descriptive Titles: Use specific terms like “Gluten-Free Chocolate Chip Cookies [Your City]” to attract local searches.
- Recipe-Structured Data: Tools like WP Recipe Maker’s Recipe Metadata Checker create rich search results with images and ratings.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Target phrases like “keto meal prep delivery Seattle” using tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ahrefs.
- Seasonal Content: Create recipes tied to holidays or local trends, such as “Pumpkin Spice Latte Cupcakes” in fall.
Leverage Social Media
Social media platforms are powerful tools for food businesses. Devon McConville of First Place Coffee increased sales by 550% through strategic Instagram posts. Focus on:
- Instagram: Share behind-the-scenes content, daily specials via Stories, and quick recipes in Reels.
- TikTok: Create engaging, authentic videos showcasing your cooking process or unique hacks.
- Facebook: Join local food groups, list products in the shop feature, and create events for pop-ups.
Encourage user-generated content by asking customers to tag your brand when sharing their purchases or recipes.
3. Network and Collaborate in the Food Industry
Collaboration amplifies your reach and builds industry relationships. Partnering with influencers, brands, and local businesses can drive growth and revenue.
Collaborate with Food Influencers and Bloggers
Identify 10-15 influencers with complementary offerings (e.g., a jam maker partnering with a baker). Propose specific collaborations like:
- Recipe swaps or co-created content.
- Joint Instagram Lives or cooking videos.
- Bundled product offerings for holidays.
These partnerships expand your audience and provide valuable industry experience.
Work with Food Brands and Eateries
- Affiliate Programs: Earn commissions through links to products like kitchen equipment on Amazon. WP Recipe Maker simplifies adding affiliate links to recipes.
- Synergistic Partnerships: Collaborate with complementary brands for cross-promotions or limited-time menu items.
- Local Collaborations: Approach cafes and specialty stores with product samples and clear partnership proposals. Start with independent shops for easier access to decision-makers.
Network at Food Events
Attend food festivals, markets, or virtual webinars to connect with customers and industry peers. Prepare business cards and wholesale information to maximize networking opportunities. Set clear goals, such as collecting contacts or securing partnerships.
4. Validate Your Business Idea Before Scaling
Starting small and testing your concept minimizes risk and ensures profitability before significant investments.
Adopt a Lean Approach
Focus on 3-5 signature products to perfect recipes and streamline production. For example, Lisa He of Borderlands Bakery discovered her decorated sugar cookies weren’t profitable after calculating labor costs. Use second-hand equipment or borrow tools to reduce startup costs.
Start Small-Scale Operations
Begin with tasting sessions to gather feedback on flavor, texture, and presentation. For delivery businesses, test routes to determine feasible zones. Sell at local markets or online platforms to gauge demand without large commitments.
Promote Limited-Time Offers
Launch limited-time products to assess market interest and production feasibility. Pre-orders validate demand and reduce waste, ensuring you only produce what’s sold.
Collect and Act on Feedback
Use feedback forms or blind tastings to identify improvements. Focus on recurring feedback (e.g., “too salty” or “better packaging needed”) to prioritize changes. Continuous improvement is key to long-term success.
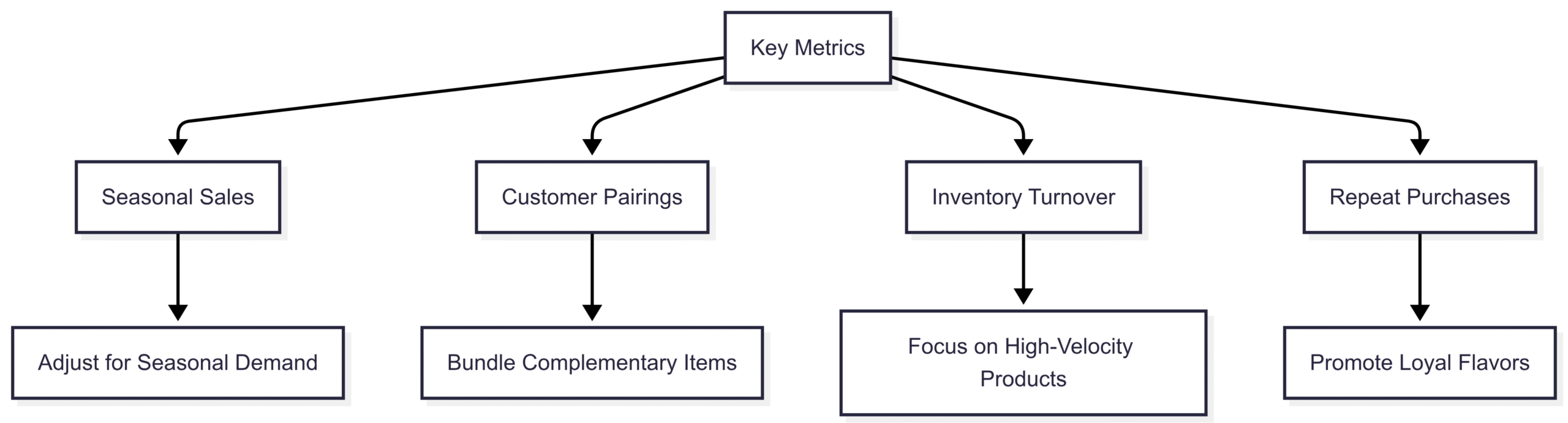
Analyze Sales and Marketing Data
Track metrics like:
- Seasonal Sales Fluctuations: Adjust inventory for temperature-sensitive products.
- Customer Pairings: Identify items frequently bought together.
- Inventory Turnover: Focus on high-velocity products to maximize profits.
- Repeat Purchase Rates: Determine which flavors drive loyalty.
Chart: Key Metrics for Food Businesses
5. Diversify Your Revenue Streams
Multiple income sources ensure resilience against market fluctuations and seasonal demand.
Home-Based Revenue Opportunities
- Digital Products: Sell premium recipe collections or meal planning services. Subscription models like a “Cookie of the Month” club create predictable revenue.
- Virtual Cooking Classes: Teach signature techniques from your kitchen, requiring minimal equipment. Classes can generate $50-150 per session.
Custom and Specialty Services
- Personalized Menu Planning: Charge $75-150 for tailored meal plans, leveraging your expertise without additional equipment.
- DIY Kits: Offer premeasured ingredient kits for customers to recreate your dishes at home.
- Seasonal Offerings: Create limited-edition holiday packages to command premium prices.
Professional Food-Related Services
- Recipe Development: Earn $250-500 per recipe for brands, with dietary specialists commanding higher rates.
- Food Photography: Offer services to other businesses at $150-300 per session.
- Consulting and Teaching: Provide startup advice or cooking classes at $50-150 hourly.
Local Partnership Opportunities
- Delivery Services: Partner with local businesses to share delivery costs and expand reach.
- Bundle Offerings: Collaborate with complementary producers for complete meal solutions.
- Consulting: Help aspiring entrepreneurs navigate permits or marketing for additional income.
Addressing Immediate Financial Needs
For those facing urgent financial challenges, such as the individual in the Reddit discussion needing money during a two-week job break, culinary side hustles can offer quick solutions. Here are practical suggestions based on the discussion:
- Donating Plasma: A quick way to earn $50-100 per session, with bonuses for first-time donors.
- Food Pantries and Community Resources: Visit local food banks, Salvation Army, or Sikh temples for free meals. Websites like www.findhelp.org or www.benefits.gov can connect you to local assistance.
- Day Labor or Restaurant Work: Apply in-person at restaurants for immediate openings or check day labor agencies like PeopleReady for quick gigs.
- Selling Food Locally: If you have basic cooking skills, sell small batches of baked goods or snacks to friends or at local markets, ensuring compliance with cottage food laws.
Conclusion
Turning your passion for food into a profitable venture is achievable with the right strategy. Whether you start a food blog, sell homemade goods, cater events, teach classes, or launch a food truck, these five proven methods offer flexibility and scalability. By choosing a profitable business model, building a strong online presence, networking strategically, validating your idea, and diversifying revenue streams, you can create a sustainable food business. Start small, comply with regulations, and leverage digital tools to reach a broader audience. With dedication and creativity, your culinary skills can become a thriving source of income.
We will meet you on next article.
Please share this 5 Proven Ways to Make Money with Food with your friends and do a comment below about your feedback.
Until you can read, Mango Kiwi Boost Smoothie






